Kaizen - Kaizen principle, Kaizen methods & importance for companies
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain...
Modular pipe systems
Attachments
5 min read
![]() Rainer Buckenmaier
:
27.Juli.2023
Rainer Buckenmaier
:
27.Juli.2023
Electronic devices have become an indispensable part of our daily lives. From smartphones and laptops to industrial automation technology, they all play a significant role in our modern world. However, while we enjoy the numerous benefits of these technologies, there is an invisible threat that can jeopardize them: Electrostatic Discharge (ESD).
In this blog article, we will dive deeper into what ESD means, how it occurs, and the risks associated with it. Additionally, we will provide tips for ESD protection and shed light on the importance of ESD testing and certification
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) refers to the sudden transfer of electric charge between two objects with different electrical potentials. This discharge can cause serious damage to electronic components and devices. As electronic devices become smaller and more sensitive, they are increasingly vulnerable to ESD. Even a small discharge can be enough to damage microchips and impair the functionality of a device.

ELF stands for "electrically conductive" and is an internal BeeWaTec designation that ensures electrical conductivity, meaning an electrical resistance of < 10^9 ohms, for components and structures. Customers must verify if this meets their requirements. The basis for designing a system to protect electronic components and assemblies is the standard according to DIN EN 61340-5-1.
Note: When designing your equipment, ensure that components such as rollers, rails, joints, etc., have the necessary conductivity. For this purpose, we offer various options and materials (e.g., galvanized joints, ELF rollers, or ELF plates).
All conductive products are marked with the ESD symbol in our new Lean catalog.
![]()
ESD symbol for marking electrically conductive components
ESD can occur in various ways. The most common cause is the friction between materials. When two materials (e.g., plastics) rub against each other or are separated, electrons can be transferred, generating an electrostatic charge. This charge remains on the surface of the materials or can be transferred to other objects when they come into contact. Electromagnetic fields or electrical discharges can also trigger ESD events.
ESD can cause significant damage to electronic devices. Microchips and other sensitive components can be damaged or destroyed by an ESD discharge. This leads to costly repairs or complete device failure.
The impact of ESD can also be latent, meaning that a device may be damaged by an ESD discharge but fail only after some time has passed. This can result in malfunctions, data loss, or even safety risks. It is essential to take ESD protection seriously and implement appropriate measures to safeguard electronic equipment and ensure the reliability of electronic systems.
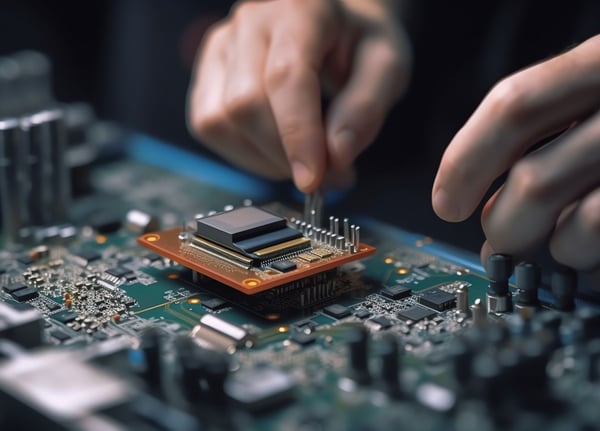

To protect against ESD, you should take the following measures, if necessary:

ESD-wristband
Whether you need ESD protection depends on your activities and environment. If you work regularly with electronic components or operate in an environment with electrostatic risks, ESD protection is essential.
Even if you are not directly involved with electronics, static discharges through clothing or other objects can still cause damage to electronic devices. It is therefore crucial to recognize the potential hazards of ESD and take appropriate protective measures.
An ESD workstation is a specially designated area (ESD protected area or EPA, also known as "electrostatic protected area") that provides ESD protection by preventing electrostatic charging. It includes antistatic work mats, conductive flooring, grounding connections, and other measures to control electrostatic charges. ESD workstations are particularly important in the electronics industry, as well as in other fields where sensitive electronic components are handled. A well-designed ESD workstation minimizes the risk of ESD events and protects electronic devices.
Note: When designing your equipment, ensure that components such as rollers, rails, joints, etc., have the necessary conductivity. For this purpose, we offer various options and materials (e.g., galvanized joints, ELF rollers, or ELF plates).
All conductive products are marked with the ESD symbol in our new Lean catalog.
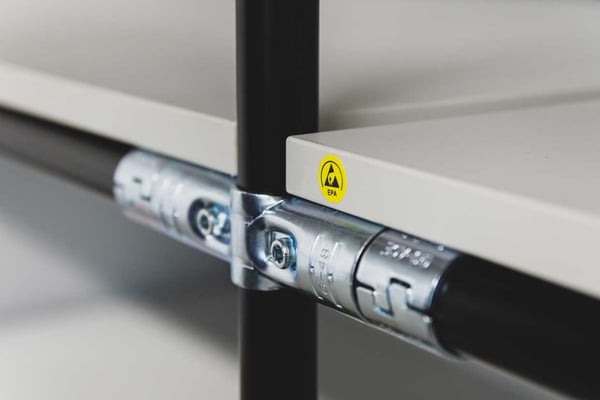

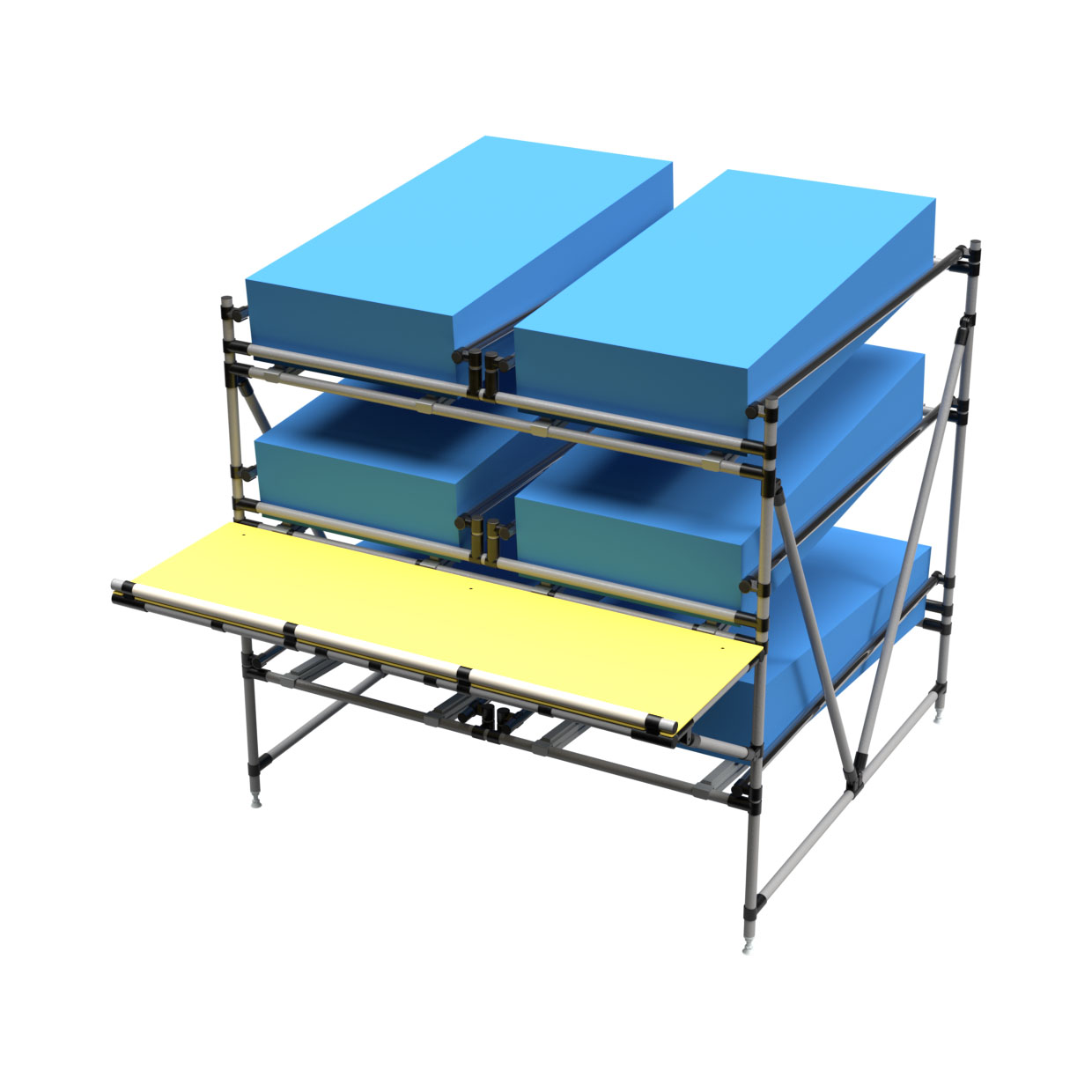
An ESD rack unit made from BeeWaTec's pipe racking system, with galvanized joints, ESD plates, and steel pipes coated with a certain amount of graphite for conductivity.
Not necessarily all attachments in an ESD workstation need to be electrically conductive. The requirements for ESD workstations depend on the specific needs and risks of the work environment. However, some attachments indeed need to be conductive to minimize the risk of electrostatic discharges and protect electronic components from ESD damage.
Here are some examples of attachments where it is recommended that they are electrically conductive:
For other attachments such as bottle holders, monitor mounts, or clipboards, electrical conductivity may not be strictly necessary. It depends on the specific situation whether these parts need to be coated or treated with ESD-safe materials.
In general, all attachments in an ESD workstation should be designed to minimize the possibility of electrostatic discharge. This means that electrically conductive components are recommended when it comes to protecting sensitive electronics, while other non-conductive attachments may be permissible as long as they meet ESD guidelines and requirements.
ESD testing is essential to ensure the effectiveness of protective measures. This includes inspecting ESD workstations and providing training to employees on ESD protection procedures. ESD certification confirms that a workstation meets the required standards for ESD protection, contributing to the quality and reliability of electronic devices.
BeeWaTec conducts testing and ESD measurements according to DIN EN 61340-5-1 during in-house assembly and provides the measurement protocol upon request.
ESD poses a real threat to electronic devices, but with appropriate protection measures, we can minimize this risk. ESD protection is essential in environments where electronic components are handled.
By designing an ESD workstation, implementing protective measures, conducting regular testing, and providing training, you can extend the lifespan of your devices, reduce downtime, and avoid costly repairs. Stay up-to-date with ESD protection practices and consistently implement them to safeguard your electronic devices and maintain their performance.
BeeWaTec offers a wide range of individual components for designing custom and electrically conductive (ELF) equipment. Contact us for more information.
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain...
At a time when companies are striving to increase efficiency and cut costs, the concept of lean management has established itself as a highly...
In an ever-changing business world, where flexibility and efficiency are crucial, the Kanban method offers a proven way to optimize work processes...