Kaizen - Kaizen principle, Kaizen methods & importance for companies
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain...
Modular pipe systems
Attachments
6 min read
![]() Jens Walter
:
23.November.2023
Jens Walter
:
23.November.2023
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain agile and competitive. Kaizen, a basic component of lean management, is proving to be an indispensable tool for organizations that want to succeed in today's world.
In this article, we explore why it is critical for organizations to embrace the principles of kaizen and lean management in order to adapt to constant challenges and increase their efficiency.
Kaizen translates as "change for the better" ("Kai" = "change" and "Zen" = "for the better") and stands for "continuous improvement" or a "continuous improvement process" (= CIP). This philosophy and method aims to constantly and gradually improve processes, products or services. It was developed in Japan (Toyota) by Masaaki Imai, particularly after the Second World War, and has since spread to various industries and organizations worldwide.

The definition of Kaizen includes the idea that small, incremental changes and adjustments in working methods or processes lead to increased efficiency, improved quality and reduced waste. This is usually done through the active participation of all employees in a company or organization, regardless of their position. The concept is often based on the PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act), which involves continuous planning, implementation, review and adjustment.
The fundamental idea of Kaizen is that continuous improvement should be an integral part of the corporate culture and not seen as a temporary project. This way of thinking is part of lean management, which should be internalized by managers in particular and passed on to individual employees. This enables companies to react more flexibly to changes, minimize waste and increase customer satisfaction.
The Kaizen principle is a fundamental concept underlying the Japanese Kaizen philosophy. It refers to the idea of improvement in business that focuses on gradual, incremental changes and adjustments in processes, products, services and ways of working. The principle emphasizes the following core ideas:
Small steps: The Kaizen principle focuses on small, incremental improvements rather than large, radical changes. Instead of making major upheavals, small adjustments and updates are made regularly.
Continuous improvement: Kaizen is a continuous and never-ending process. Organizations and individuals should continuously strive to improve their way of working and their results.
Participation of all employees: Every employee, regardless of their position in the organization, is encouraged to participate in identifying opportunities for improvement. This creates an environment in which employees are actively involved in shaping and improving their work.
Process orientation: The Kaizen principle refers not only to the improvement of products or services, but also to the continuous optimization of business processes and procedures.
Customer orientation: Kaizen takes into account the needs and expectations of customers and strives to continuously improve the quality and value of products or services in order to increase customer satisfaction.
Measurable results: Improvements should be traceable and measurable so that the impact on performance and quality can be monitored and evaluated.
Kaizen offers a multitude of benefits for companies, regardless of their size or industry. Here are some of the key benefits of Kaizen:
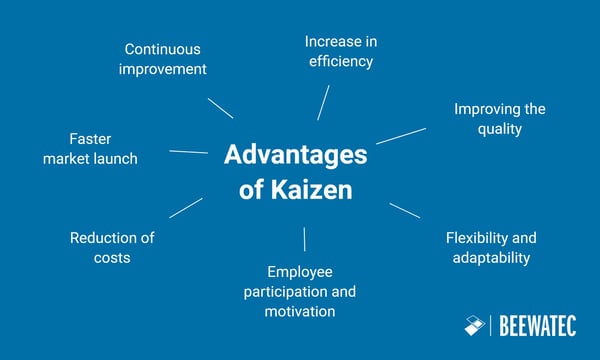
Continuous improvement: the key benefit of Kaizen is in its name itself. The method promotes a culture of continuous improvement in which small, incremental steps lead to processes, products and services being constantly optimized. This enables companies to adapt flexibly to changing requirements.
Increasing efficiency: Kaizen aims to minimize waste and maximize efficiency. By identifying and eliminating unnecessary steps in processes, companies can make their operations leaner and more efficient.
Quality improvement: The constant review and adjustment of work processes in Kaizen lead to better quality of products and services. Errors are identified and rectified more quickly, which increases customer satisfaction.
Employee involvement and motivation: Kaizen involves employees at all levels of the organization. By involving the workforce in the continuous improvement process, employees feel more connected to their contribution to the company's success, which increases motivation and productivity.
Cost reduction: By identifying waste and optimizing processes, companies can reduce costs. This includes not only direct production costs, but also indirect costs such as stock levels and waiting times.
Faster time to market: The agile nature of Kaizen enables companies to respond more quickly to market demands. Through continuous improvement, products and services can be developed, tested and brought to market faster.
Flexibility and adaptability: Companies that practice Kaizen are better able to adapt to change. Constantly evaluating and adapting processes makes organizations more flexible and resilient to unforeseen challenges.
Essentially, all kaizen methods are designed to make small, incremental changes to processes, products and services. Here are some of the most important kaizen methods:
PDCA-Zyklus (Plan-Do-Check-Act):
Plan: Define the goal and process for improvement.
Do: Put the plan into action.
Check: Evaluate the results and gain experience.
Act: Implement necessary changes based on lessons learnedAct (Handeln).
5S method:
Sort (Seiri): Eliminate what is unnecessary.
Systematize (Seiton): Organize the workplace efficiently.
Clean (Seiso): Clean the workplace.
Standardize (Seiketsu): Establish standards for order and cleanliness.
Self-discipline (Shitsuke): Maintain discipline and continuous improvement.
Kaizen workshops: Organized events where teams come together to analyze processes, identify problems and develop solutions.
Gemba walks: Direct observation of workplaces and processes to identify problems and find opportunities for improvement.
Kanban: Visualizing work processes using cards to identify bottlenecks and flow issues.
Quality groups: Small working groups of employees who meet regularly to discuss problems and develop solutions.
Standard operating procedures (standard work): Establish standardized procedures to promote efficiency and consistency.
Andon system: A visual control system that signals problems in the production process to enable an immediate response.
CIP (Continuous Improvement Process): A systematic approach to continuous improvement of processes and products.
Hoshin kanri (target management): Eine Methode zur strategischen Planung, Umsetzung und Überwachung von Unternehmenszielen.
Value Stream Mapping: Visualization of processes to identify waste and optimize the value stream.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): An approach to maintenance that aims to make machines more efficient and reduce downtime.
These Kaizen methods can be used individually or in combination to promote continuous improvement in various aspects of an organization
Kaizen is more than just a Japanese method; it is a lean management mindset and philosophy similar to total quality management. As such, it influences the way managers and employees view and approach challenges. Kaizen can also be described as a philosophy of life and work that seeks to systematically identify and implement suggestions for improvement in order to break down the current standard.

Management plays a crucial role in the introduction and implementation of Kaizen in a company. It includes setting clear goals, allocating resources and supporting employees in applying Kaizen principles. Managers must foster open communication and create an environment where employees are encouraged to develop creative solutions and propose innovative ideas.
Innovation is also an essential part of Kaizen. The continuous search for improvement often implies innovative approaches, be it in terms of products, processes or services. In addition, the introduction of a kaizen mindset can positively influence the attitude of employees towards internal change and new ideas.
The 5S method and Kaizen are two lean management approaches that are closely related and often used together to drive continuous improvement in organizations. Here is how they are related:
Common goal of continuous improvement:
Both 5S and Kaizen share the fundamental goal of continuous improvement. Both approaches aim to reduce waste, increase efficiency and improve the quality of processes, products or services.
5S as the basis for Kaizen:
The 5S method often serves as the basis for Kaizen activities. The 5S includes the steps of sorting, systematizing, cleaning, standardizing and self-discipline. These steps create a structured and organized work environment, which forms the basis for effective Kaizen initiatives.
Order and efficiency through 5S:
By implementing the 5S method, workplaces are organized and tidy. This contributes to a clear working environment, making it easier to identify waste and inefficiencies. Order through 5S creates the conditions for successful implementation of Kaizen.
Employee involvement:
Both 5S and Kaizen emphasize the participation of all employees in the improvement processes. Implementing 5S often requires the active participation of employees, which creates the foundation for a collaborative culture that is critical to the success of Kaizen.
Standardization and sustainability:
The 5S method involves creating standards for order and cleanliness, which lays the foundation for sustainable improvements. Standardization ensures that the improvements achieved are not just temporary, but are permanently anchored in the work processes.
Identification of opportunities for improvement:
By implementing 5S, irregularities and waste become more obvious, paving the way for Kaizen. Employees are encouraged to identify opportunities for improvement and in an organized work environment they can respond more easily to change.
Overall, the 5S method and Kaizen work hand in hand, with the structured order and standardization provided by 5S providing the foundation for the continuous improvements sought by Kaizen. Companies that combine both approaches create an environment that promotes flexibility, efficiency and a culture of continuous improvement.
By using lean solutions, companies can optimize their work processes and achieve efficiency gains. BeeWaTec's lean equipment is designed to minimize waste and support continuous, smooth production - a core element of Kaizen

BeeWaTec offers modular solutions that enable companies to design equipment such as flow racks, assembly workstations and transport trolleys according to their specific requirements. This ensures adaptability, even after the solutions and systems have been implemented and used. No matter what ideas come up in the future or what new requirements arise, the BeeWaTec modular system offers the opportunity for continuous improvement.
Kaizen is of crucial importance in the B2B sector. By continuously optimizing processes, products and services, Kaizen enables companies to remain competitive in a changing market environment. Increased efficiency, cost reductions and a strong customer focus are key factors that make kaizen an indispensable tool in the B2B sector. The ability to continuously adapt and improve not only ensures efficiency, but also strengthens the development of innovations in the long term.

With our modular system you can implement any solution you need. Discover your possibilities, existing solutions or build your own material flow system with BEEVisio in 3D.
In a world where markets are changing rapidly and competition is more intense than ever, organizations are looking for effective methods to remain...
At a time when companies are striving to increase efficiency and cut costs, the concept of lean management has established itself as a highly...
The material flow is an important part of every production and logistics. It describes the physical movement of materials, products and goods through...